IMAGING PROCEDURES AVAILABLE
quality images for many types of
exams.
“The 3-T MRI is ideal for ortho-
pedic and neurologic exams,” said
Jennifer Neely, director of Kootenai
Outpatient Imaging. “It offers
superior image quality, it’s quieter
than the older machines, and it is
faster, which means patients spend
less time on the scanner table.”
Patient safety is also a top priority
for Kootenai’s Imaging Services.
Over the past several years, the team
has implemented new equipment,
tools and staff protocols that improve
their ability to monitor and lower a
patient’s exposure to the radiation
that is produced by some imaging
modalities, including x-ray and CT.
“When we talk about providing
quality service, we talk about how
to keep patients safe and strategize
lower patient radiation dose,”
Jennifer said. “It’s an ongoing
discussion; we are always looking
for ways to minimize dose and to
train our staff so they know ways to
reduce dose themselves.”
Nearly all of the imaging equip-
ment is centrally connected to a
software program that monitors and
analyzes radiation dosage for every
patient procedure. If radiation dos-
ages exceed set limits, the system
alarms the technician in real
time so dosages can be corrected
accordingly.
“We monitor radiation exposure
very carefully, and as a result,
we’ve been able to keep average
patient doses well below American
College of Radiology guidelines,”
Mike said.
It’s all part of Kootenai’s commit-
ment to providing patients with the
best experience possible.
“We try to treat every patient
as an individual,” Jennifer said.
“Even though this is something
we do every day, we understand
that this could be something very
scary for them. We try to educate
all patients about why they are
here and walk them through their
studies so they know what to
expect.”
M A K E A N A P P O I N T M E N T T O D A Y
for your
annual screening mammogram. Visit
KH.org/imaging, or call
(208) 625-6300
.
Available imaging procedures include:
◗
◗
X-ray
uses electromagnetic radiation to capture
images of dense structures inside the body. It is
often used to study bony structures, the gastro-
intestinal system, and kidney or bladder function
(with contrast material).
◗
◗
Ultrasound
sends sound waves into the body.
These waves bounce off body structures and
produce real-time images on a monitor. It is often
used to study unborn babies, internal organs,
muscles and other soft tissue structures.
◗
◗
Computed tomography (CT)
combines x-rays and
computers to produce 2- and 3-D images. It helps
in the diagnosis of various symptoms or condi-
tions and guides treatment decisions.
◗
◗
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
uses a powerful
magnet, radio waves and computer technology to
produce detailed, multidimensional images. It’s a
versatile tool used in the diagnosis and treatment
of many medical conditions.
◗
◗
Nuclear medicine
is a radiology subspecialty that
combines the use of radioactive tracers and imag-
ing technology to study the anatomy and function
of organs.
◗
◗
Mammograms
are x-ray exams used to screen for
breast cancer.
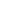
Dillon Smedley is an
imaging specialist at
Kootenai Health. Here
he is pictured with one
of Kootenai's newest
CT scanners, which
combines x-rays and
computers to produce
2- and 3-D images.
KH . ORG
17